MOLDING MATERIALS
Choosing the right plastic material is a critical step in any custom injection molding project. The performance, durability, and appearance of your final part depend heavily on this decision.
Before selecting a material, consider key factors such as:
✎ Part function and application
✎ Required strength, flexibility, and impact resistance
✎ Environmental exposure (e.g., UV, heat, chemicals)
✎ Aesthetic requirements (color, surface finish)
✎ Regulatory or industry standards (e.g., food-grade, medical, flame retardant)
Different plastics exhibit unique behaviors during molding and in end-use conditions. One often-overlooked factor is material shrinkage. Each resin shrinks at a different rate as it cools, which directly affects dimensional accuracy.

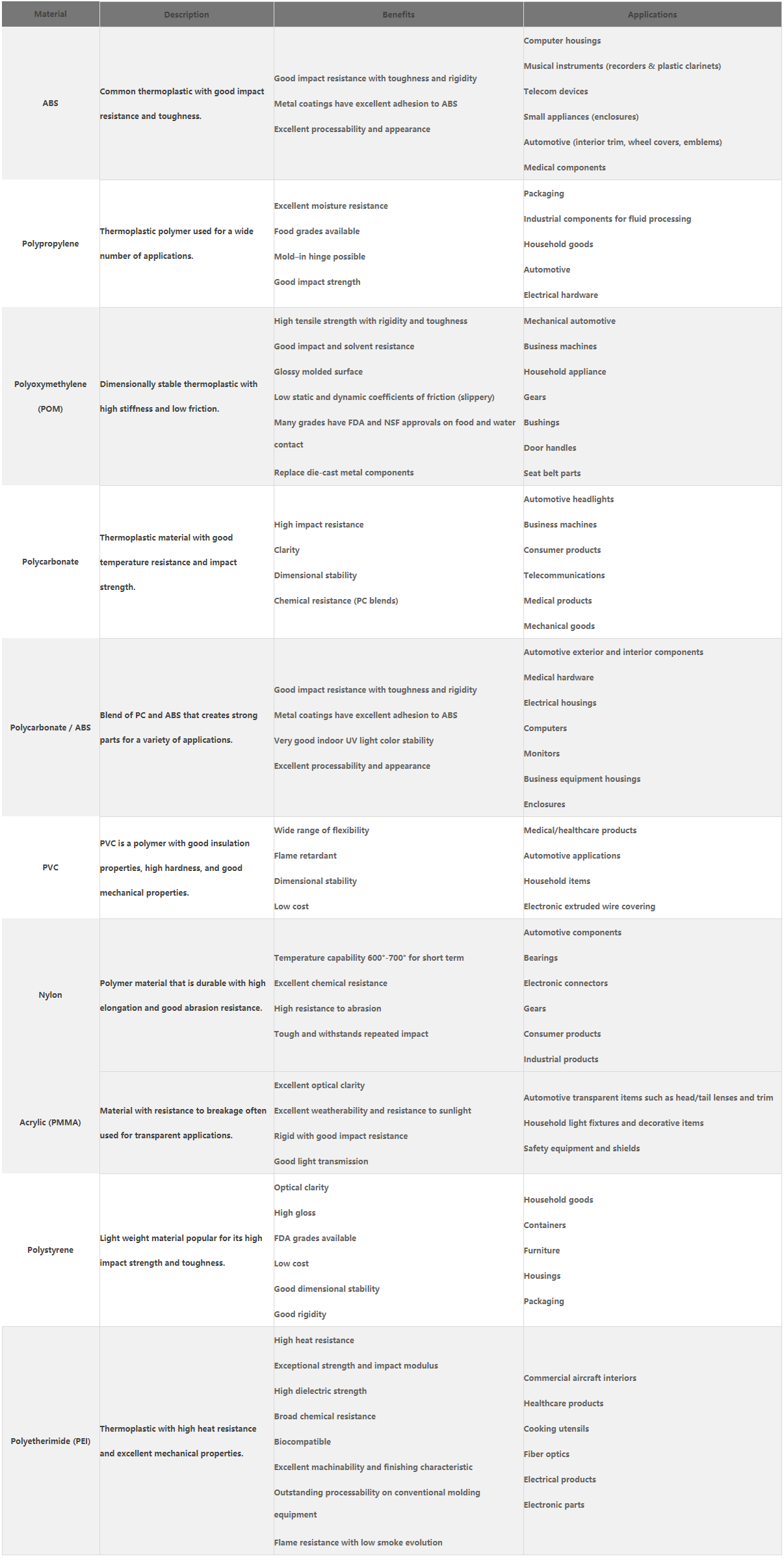
To help guide your selection, below is a table of the most commonly used thermoplastics in injection molding, along with their key properties and typical applications.